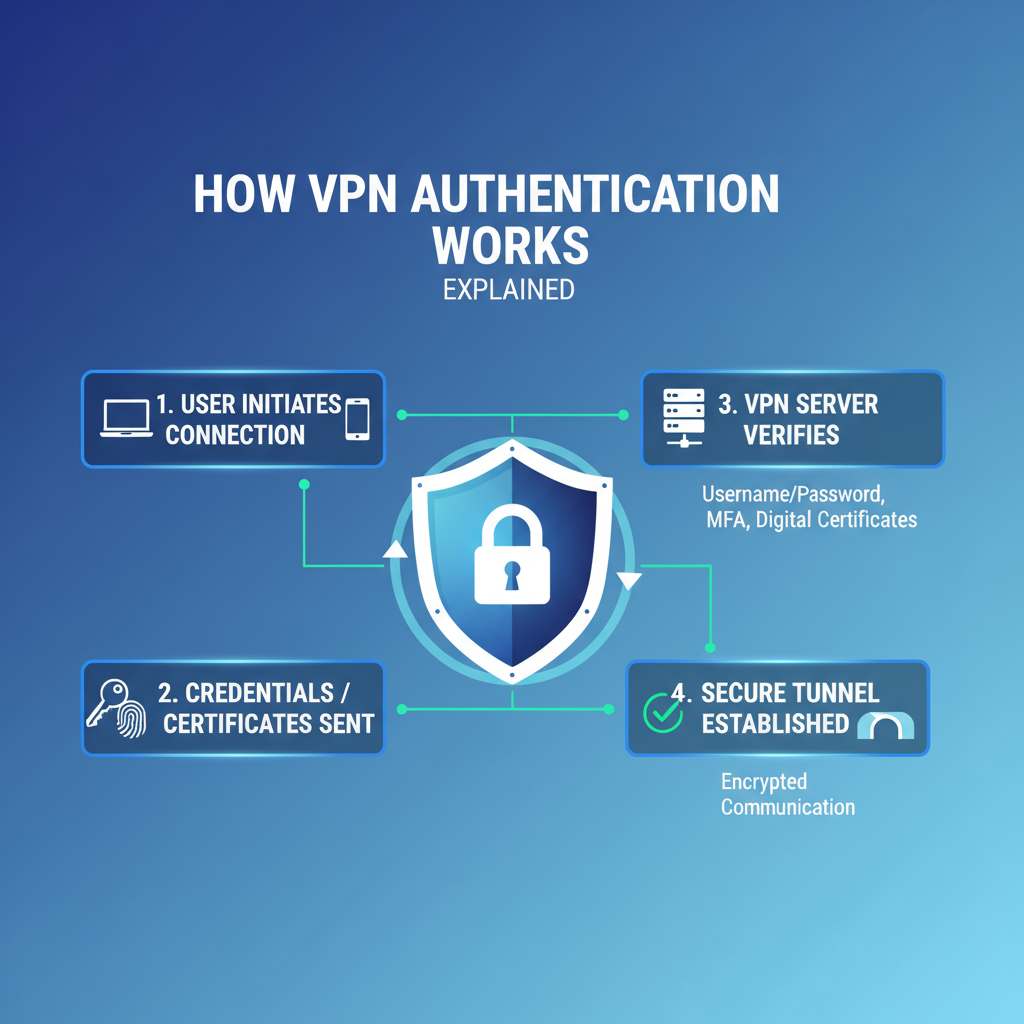
When using a Virtual Private Network (VPN), understanding how VPN authentication works is crucial for both security and privacy. VPN authentication is the process by which users confirm their identity before accessing the network. Let’s dig deeper into the different methods and how they function.
What is VPN Authentication?
VPN authentication ensures that only authorized users can connect to the VPN. It protects sensitive data and maintains network integrity. This process typically involves verifying credentials like usernames, passwords, or digital certificates. If authentication fails, access is denied, keeping your data secure.
Types of VPN Authentication Methods
There are several methods to authenticate users, each with its own level of security and complexity. Here are the most common:
- Password-Based Authentication: This is the simplest and most widely used method. Users provide a username and password. While easy, this method is vulnerable to hacking if passwords are weak.
- Certificate-Based Authentication: This method uses digital certificates to verify users. Users must install a certificate on their device, providing a higher level of security. If an unauthorized user tries to connect, they won’t have the valid certificate.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security, 2FA requires users to provide two forms of identification. This could be a password plus a one-time code sent to their phone. Even if a hacker gets the password, they still need the second factor to access the VPN. To learn more about this security measure, check out our guide on what is two-factor authentication (2FA) and how it works.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Similar to 2FA, MFA can involve multiple factors such as something you know (password), something you have (mobile device), and something you are (fingerprint). This is one of the toughest security setups.
How Does VPN Authentication Work?
The process of VPN authentication involves multiple steps, which might vary slightly depending on the method used. Here’s a general overview:
- User Request: When you try to connect to a VPN, your device sends a request to the VPN server.
- Credential Transmission: Your device transmits the authentication credentials to the VPN server. This is often done via a secure protocol to keep data safe during transfer.
- Server Verification: The VPN server checks the submitted credentials. If you’re using password-based authentication, it compares the password against the stored records. For certificate-based methods, it checks the validity of the certificate.
- Access Decision: If verification is successful, the server establishes a secure tunnel for you to use. If not, access is denied, and you cannot connect.
Important Protocols Used in VPN Authentication
Several protocols support VPN authentication, each offering different features and security levels. Some of the widely used protocols include:
- OpenVPN: Known for its flexibility and strong security, OpenVPN uses SSL/TLS for encryption and supports various authentication methods.
- PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is easier to set up but less secure compared to other protocols. It mainly relies on password authentication.
- L2TP/IPsec: Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol combined with IPsec offers better security by encrypting the data traffic.
- IKEv2/IPsec: This protocol provides robust security and is known for its speed and stability during connection interruptions.
To understand more about how these protocols function, check out our article on how does a VPN work.
Why is VPN Authentication Necessary?
VPN authentication safeguards your data by preventing unauthorized access. As cyber threats continue to evolve, having a secure authentication method is essential for protecting your sensitive information. Without proper authentication, your data could easily fall into the wrong hands. To learn more about various threats, see our guide on types of cyber threats explained.
Understanding how VPN authentication works is vital in today’s digital landscape. Each method has its own advantages, and selecting the right one greatly impacts your security. By employing robust authentication strategies, you can ensure that only authorized individuals access your network, keeping your data safe and secure.
The Importance of Secure VPN Protocols
In today’s digitally-driven world, online security has become a priority for many individuals and businesses alike. As people rely more heavily on the internet for communication, work, and various transactions, using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) has become essential. Secure VPN protocols play a crucial role in ensuring that your data remains safe and private while you are navigating the online landscape.
VPN protocols are rules that dictate how data is transmitted between your device and the VPN server. Different protocols offer varying levels of security and speed, making it important to choose the right one based on your needs. Let’s explore why secure VPN protocols matter and what they can do for you.
First and foremost, using secure VPN protocols helps to protect your online privacy. When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted. This means that anyone trying to intercept your data, such as hackers or even your Internet Service Provider (ISP), will not be able to see what you’re doing online. By using protocols such as OpenVPN or IKEv2, you can ensure that your personal information remains confidential. For more information on encryption, see our guide on VPN encryption explained for beginners.
Additionally, a robust VPN protocol helps to prevent unauthorized access to your information. When sensitive data such as passwords or credit card numbers are transmitted without proper security measures, they are vulnerable to cyber threats. Choosing a VPN that implements secure protocols means you add a layer of defense, ensuring that such information is protected both during transmission and at rest.
Another significant advantage of secure VPN protocols is the ability to bypass geographical restrictions. Sometimes, content is restricted based on your location. When you connect to a secure VPN server, you mask your IP address, making it look like you are accessing the internet from a different location. This is particularly beneficial for streaming services or websites that may have content limitations based on your country. By leveraging the right VPN protocols, you can access a broader range of content without compromising your security.
Here’s a brief overview of some of the most secure VPN protocols you might encounter:
- OpenVPN: This is one of the most widely used and trusted protocols. It combines strong encryption with high speed and flexibility, making it suitable for most uses.
- L2TP/IPSec: This combination offers better security than traditional L2TP. It provides encryption but may not be as fast as OpenVPN.
- IKEv2/IPSec: This protocol is known for its resilience. It’s particularly effective for mobile devices as it can reconnect quickly when a connection is lost.
- SSTP: This protocol uses SSL to provide a secure connection and works well for bypassing firewalls. To learn more about SSL, check out our article on what is SSL and TLS explained for beginners.
- PPTP: While it’s one of the oldest protocols and can offer decent speeds, it’s less secure compared to the others due to weaker encryption.
When selecting a VPN service, it’s vital to consider not only the speed but also the level of security the protocol provides. A faster connection may be tempting, but if it comes with reduced security, it could leave you vulnerable in the online world. Prioritize your online safety over speed, particularly when handling sensitive information. Some users wonder if a VPN makes internet slower, but modern protocols balance speed and security effectively.
Moreover, secure VPN protocols facilitate safe remote work. As organizations increasingly adopt remote working frameworks, using a secure connection becomes essential for accessing company networks. Without a trusted VPN protocol, employees may expose themselves and their organizations to data breaches or unauthorized access. By using encryption and secure transport protocols, companies can establish a safer remote working environment. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks.
In an era where digital threats are on the rise, understanding how secure VPN protocols work can empower you to make informed decisions about your online activities. By prioritizing a VPN that utilizes the best protocols, you are taking a proactive step in safeguarding your digital life. Remember, when it comes to your online safety, every detail counts, and utilizing secure VPN protocols is a fundamental part of that equation.
Your online security is in your hands. Make the right choice today and opt for a VPN that values your privacy and security with robust protocols.
Different Types of VPN Authentication Methods
When you connect to a Virtual Private Network (VPN), authentication plays a vital role in ensuring that your information remains secure. There are several methods for VPN authentication, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these methods can help you choose the right VPN service for your needs.
Username and Password Authentication
This is the most common and straightforward method of VPN authentication. You simply enter a username and password to access the network. While this method is easy to use, it can be vulnerable to breaches if passwords are weak or stolen.
Pros:
- Easy to set up and use.
- Widely supported by most VPN services.
Cons:
- Can be susceptible to phishing attacks.
- If passwords are weak, it poses a security risk.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to the traditional username and password login method. After entering your credentials, you must also provide a second piece of information, often in the form of a code sent to your phone or generated by an app.
Pros:
- Significantly increases security.
- Protects against unauthorized access even if the password is compromised.
Cons:
- Can be inconvenient if you don’t have immediate access to your second factor.
- May slow down the login process.
For a detailed explanation of how 2FA works, check out our guide on what is two-factor authentication (2FA) and how it works.
Certificate-Based Authentication
This method uses digital certificates to verify the identity of a user. Each client device is assigned a unique certificate, which must be presented and validated against the VPN server during the connection process.
Pros:
- Highly secure as it eliminates the need to store passwords.
- Colleges and businesses often use certificates to manage devices efficiently.
Cons:
- More complicated to set up compared to password-based methods.
- Requires certificate management skills.
To learn more about verifying digital certificates, see our article on how to verify website security certificate.
Pre-Shared Key (PSK) Authentication
In PSK authentication, both user and VPN server agree on a key before establishing a secure connection. This key is used to encrypt your data throughout the session.
Pros:
- Offers strong encryption when configured correctly.
- Easy to implement for small networks.
Cons:
- If the key is compromised, the entire network is at risk.
- Not scalable for larger organizations.
OAuth-Based Authentication
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation often used for token-based authentication. Users sign in through an external service provider, like Google, which verifies their identity and sends a token back to the VPN.
Pros:
- Convenient, as users can log in without needing a separate username and password.
- Reduces the risk of password fatigue and reuse.
Cons:
- The security of the VPN relies heavily on the external provider.
- Users must trust the provider with their credentials.
RADIUS Authentication
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) offers centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for users who connect and use a VPN service. This method involves a RADIUS server that verifies user credentials before granting VPN access.
Pros:
- Centralizes user management, making it easier for businesses.
- Supports multiple authentication methods for flexibility.
Cons:
- Requires a more complex setup.
- Not ideal for smaller organizations without IT support.
Each authentication method comes with its own challenges and benefits. By understanding how VPN authentication works, you can make informed decisions about securing your online activities effectively. Always choose a method that fits your needs in terms of security, convenience, and scalability.
Common Challenges in VPN Authentication and Solutions
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are essential for protecting your online privacy, especially in an age where cyber threats are rampant. However, while VPNs provide a layer of security, authentication processes can pose various challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring a smooth and secure experience when using a VPN.
Weak Passwords and Credential Management
One of the most common challenges in VPN authentication is the use of weak passwords. Many users opt for simple passwords that are easy to remember but also easy for hackers to guess. This can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Solution: Implementing strong password policies can greatly enhance security. Encourage the use of complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, employing a password manager can help users generate and store secure passwords without the need to memorize them.
Lack of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Single-factor authentication, where users only provide a username and password, is no longer sufficient for robust security. The absence of multi-factor authentication is a significant vulnerability that hackers exploit.
Solution: Incorporate multi-factor authentication in your VPN setup. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a text message code or an authentication app. With MFA, even if a password is compromised, unauthorized users are still prevented from accessing the VPN.
Outdated Authentication Protocols
Using outdated or insecure authentication protocols can expose VPN users to various attacks. Some outdated protocols may not support modern encryption standards or things like MFA, making them less reliable.
Solution: Regularly update your VPN’s authentication protocols to support strong options such as OpenVPN or IKEv2. Monitoring and upgrading software ensures that your VPN uses the latest security features and fixes any known vulnerabilities.
Device and Platform Compatibility Issues
Another challenge is the compatibility of devices and platforms with VPN authentication methods. Sometimes, a VPN might work seamlessly on one device but face issues on another, such as mobile phones or different operating systems.
Solution: Choose VPN services that offer cross-platform support and are compatible with a wide range of devices. Additionally, ensure that your authentication methods are consistent across platforms. Providing clear instructions for different devices can also help users navigate any issues they encounter. For iPhone users, our guide on how to use VPN on iPhone without app might be helpful.
User Training and Awareness
A lack of awareness among users about secure practices related to VPN authentication can lead to lapses in security. Users may not know how to recognize phishing attacks or understand the importance of secure credentials.
Solution: Conduct regular training sessions for users to educate them about VPN best practices. This includes how to create strong passwords, recognize phishing attempts, and the importance of using multi-factor authentication. Keeping users informed is a key component in securing your network.
Network Performance and Connectivity Issues
Authenticating through a VPN can sometimes lead to slower internet speeds or connectivity issues, which can frustrate users. These performance-related problems may arise during peak usage times or due to inadequate server resources.
Solution: Optimize VPN performance by choosing servers that are not overloaded. Using higher-bandwidth servers can improve the speed of authentication and overall connectivity. Additionally, keeping the software updated and selecting protocols that offer better performance can help mitigate these issues. To understand more about speed concerns, see our article on does VPN make internet slower.
Cost Considerations
Some VPN providers may charge extra for advanced authentication features or multi-factor authentication options, which can deter users. This can leave them exposed to risks if they opt for cheaper, less capable solutions.
Solution: Evaluate the cost versus the benefits of investing in a reputable VPN service that provides comprehensive authentication options. Although it may involve a higher upfront cost, prioritize security to protect sensitive information, which can save you money and hassle in the long run. Our comparison of free vs paid VPN services can help you make an informed decision.
While VPN authentication can present several challenges, implementing effective solutions can significantly strengthen your security posture. By addressing these common issues, you can enjoy a safer online experience while using a VPN service.
Future Trends in VPN Technology and Authentication
The landscape of virtual private networks (VPNs) has been evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing cybersecurity threats. As the internet becomes more interconnected, the need for robust VPN technology and authentication methods has never been greater. Understanding future trends in VPN technology can help you stay ahead of security challenges and ensure your online privacy. Here’s what to look out for.
Increased Use of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to play a significant role in shaping VPN technology. These technologies can analyze network traffic patterns, helping VPN providers identify potential threats and anomalies in real-time. As a result, users can expect improved security measures, such as:
- Automated threat detection.
- Personalized security protocols based on usage patterns.
- Adaptive encryption standards that respond to emerging threats.
This integration of AI not only enhances security but also optimizes VPN performance, ensuring a smoother user experience.
Stronger Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Protocols
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, the importance of multi-factor authentication grows. Future VPNs will likely implement advanced MFA methods that go beyond mere passwords. You can expect to see:
- Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
- Geolocation-based authentication to verify user location.
- One-time password (OTP) applications for added security.
These enhancements will make unauthorized access much more challenging for cybercriminals, thus safeguarding your online activity.
Enhanced Privacy Features
With increasing scrutiny on privacy laws and data collection practices worldwide, VPN providers are focusing on offering enhanced privacy features. Users are likely to benefit from:
- No-logs policies that ensure your online activities remain entirely private.
- Advanced encryption algorithms to keep data secure from prying eyes.
- Integrated ad-blocking and malware protection capabilities.
These features make your browsing experience both secure and more enjoyable by minimizing interruptions from ads and potential malware threats.
Decentralized VPN Solutions
Decentralization is a trend gaining traction across various technologies, including VPNs. Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) operate on a network of servers run by users rather than by a single company. This approach offers several key advantages:
- Reduced risk of data leaks due to local server management.
- Greater resilience against censorship and geo-blocks.
- Opportunities for users to earn money by sharing their bandwidth.
As dVPN solutions become more mainstream, they may provide users with more control over their online privacy.
Integration with IoT Devices
The explosive growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has led to a pressing need for robust security solutions. The future of VPN technology will likely involve seamless integration with IoT devices, ensuring that everything from smart home gadgets to wearables is shielded from attacks. Expect to see:
- VPN configurations specifically designed for IoT ecosystems.
- Automated security updates to protect connected devices.
- Network segmentation to isolate IoT traffic from other networks.
This approach will enhance the overall security of interconnected devices, which are often the target of cyberattacks.
Focus on Speed and Efficiency
As VPN usage grows, so does the demand for speed and efficiency. Future trends will likely emphasize optimizing connection speeds and reducing latency. Innovations to watch for include:
- Protocols designed specifically for faster data transmission.
- Server upgrades and expansions to distribute traffic effectively.
- Improved load balancing techniques to prevent bottlenecks.
With these advancements, users will enjoy faster and more reliable connections, making VPNs practical for various online activities.
To understand more about how VPN usage affects your online experience, check out our article on what really happens when you use a VPN all the time.
Staying informed about these trends helps you choose the best VPN technology for your needs. As the digital world continues to evolve, investing in a robust, secure VPN service will become increasingly essential for safeguarding your online privacy and security.
Conclusion
Understanding how VPN authentication works is crucial in today’s interconnected world. As you’ve learned, the foundation of secure online activities relies significantly on robust VPN protocols. These protocols not only safeguard your data but also enable seamless connections to remote servers. By exploring various VPN authentication methods, such as password-based, certificate-based, and multi-factor authentication, you can choose the right level of security for your needs.
It’s important to recognize the common challenges that arise within VPN authentication, like potential vulnerabilities and user errors. Fortunately, you can mitigate these issues through regular updates and employee training, ensuring that your VPN remains secure and user-friendly.
Looking ahead, the future of VPN technology and authentication is promising, with advancements like artificial intelligence and machine learning on the horizon. These innovations will undoubtedly enhance security measures, making VPN connections even more resilient against cyber threats.
Staying informed about these developments can empower you to make strategic decisions regarding your online safety and privacy. By implementing effective VPN authentication methods and staying abreast of future trends, you can navigate the digital landscape with confidence, knowing that your data is well-protected. Embracing these proactive strategies ensures that you’ll be equipped to handle whatever challenges come your way in this ever-evolving cyber environment.
For more information on related topics, consider exploring our articles on what is cybersecurity, how to prevent VPN leaks and DNS leaks, and the difference between VPN and proxy.